Diary Chapters
Energy Everywhere
Wise Words
Energy and persistence conquer all things.
Benjamin Franklin
FEELING ENERGETIC?
Imagine how different our lives would be without energy. Did you
know that the energy from your power point comes from different
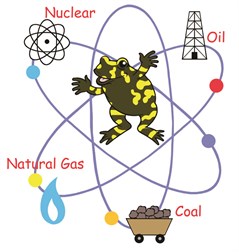
sources? Energy can be 'renewable' or 'non-renewable'.
Non-renewable sources are materials buried in the ground such as
coal, gas and oil (also called 'fossil fuels'). Fossil fuels are
formed from plants and animals that lived millions of years
ago.
Most of the energy we use today is generated through the burning
of fossil fuels. It's pretty reliable and cheap, but releases
greenhouse gases and pollution into our air. Another downside is
that once all fossil fuels from the ground are used up, they are
gone. It takes millions of years for the fuel to form.
Renewable energy can be made from the sun (solar), rivers and
oceans (hydro), wind, plants (biomass) and our planet's hot centre
(geothermal) sources - which will never run out. This renewable,
green energy releases fewer greenhouse gases into the atmosphere.
It already provides around 16% of global energy supply. Exploring
more renewable energy ideas will help move to a cleaner energy
future. Research organisation Beyond Zero Emissions are leading the
exploration and have lots of great information on their website.
Here is a funny video that explains
the difference between these two sorts of energy!
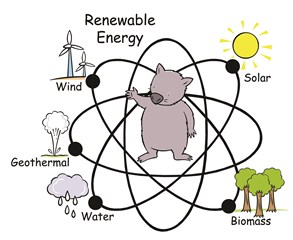
FIVE SOURCES OF RENEWABLE ENERGY
1. Solar power: The sun shines on
"photovoltaic" or "PV" panels which produce an electric
current.
Batteries are used to store energy for use at night. In another
method curved mirrors are used to concentrate sunlight to heat up
water and produce steam that can power a generator.
2. Wind power: wind pushes the blades of wind
turbines and makes them spin. The rotation of the blades generates
electricity.
3. Hydro-electric power: water movement from
rivers and ocean waves pushes giant turbines. The rotation of the
turbines creates electrical energy.
4. Geothermal power: Underground heat from the
centre of our planet can be used directly to heat buildings or can
be used to create steam to push turbines and create
electricity.
5. Biomass power: Plants and rubbish are burnt to
heat up water and create steam that can push turbines. In another
method, plants are converted into biofuels such as methane or
ethanol.
SOLAR POWER IN AUSTRALIA
If it's so great, why isn't everyone using solar power? Well,
solar technology is still very new, and sometimes it takes time for
new things to catch on. Plus, even though solar electricity is a
lot cheaper to run, it can be expensive to install initially.
At Green Cross Australia, we think solar energy is definitely
the future of electricity in Australia, but we know it needs to be
more affordable. That's why we've introduced 'Every
Rooftop' - this green energy initiative works out how
households and businesses can use solar energy to best save money,
electricity and the environment.
Solar leasing
Depending on a business or home's energy use, it can be cheaper
to lease a solar system, instead of buying one upfront.
Every Rooftop allows people to install solar - for free - by
leasing the solar system. So the energy company pays to install the
system and your household or business can rent it from them. That
way, you can benefit from a smaller electricity bill and can help
the environment, without having to pay a lot of money to install
the solar system yourself.
Solar leasing is new in Australia but has been big in the US for
years; solar leasing accounts for over 75% of new residential solar installations in
California.
Can you find out more about solar leasing vs solar buying? Is
one better than the other? How are they different?
Do a count - how many appliances do you have at home that use
energy? Are they completely turned off or do they use standby power
(some power a little light even when they appear to be off)? How
can you keep them off when they aren't in use?
Hold an e-waste day at school. Charge a gold coin donation to
collect the items. Dispose of them properly and use the money for a
green project.
Fridges, appliances and your house's hot water heater use almost
half of the energy consumed at home.
In January 2014, the number of Australian homes with solar power
systems passed the two million mark.
Sarah Costanzo & Laura Gooding, St Joseph's Primary,
Corinda
Two creative and enterprising students thinking
outside the square for the planet! As an
extra project, the girls made a range of items by recycling
materials and sold them to raise money for Algalita Marine Research
Institute while also raising awareness in their school community
about the importance of marine research. Check out their video here!
Nominate Energy Monitors at school. What kinds of things could
they do to reduce your school's energy use? Talk on assembly, run
competitions,
make reminder 'switch off' stickers?
Develop a school project to reduce energy during peak hours when
it really matters. Don't forget to tell us what you're
doing to be crowned a Green Lane Hero!
Research
how an electric car works? Can you make a model and share it with
your friends and family?
THE ENERGY SWITCH
 We
can reduce the carbon dioxide we release into our air by using
cleaner forms of energy, using less energy hungry-technology or
capturing the carbon before it escapes into the atmosphere.
We
can reduce the carbon dioxide we release into our air by using
cleaner forms of energy, using less energy hungry-technology or
capturing the carbon before it escapes into the atmosphere.
Carbon can be captured through simple actions
such as planting a tree, or more complex ones such as pumping
carbon gases underground (also called 'geosequestration'). Large
manufacturing plants, airplanes, big buildings, homes and cars
could all be powered by clean, renewable energy.
Find out how much carbon you use up with this great Kids Carbon Counter!
|
BUILDING DESIGN
Our buildings use huge amounts of energy, mainly for heating and
cooling. This can be reduced if they are designed carefully by
facing the right direction, using insulation, planting trees and
avoiding windows on the west side. Appliances should be energy
efficient. Well designed buildings need less energy! So think about
it, how would you design your home? You can start
to research the facts on the 'Envirotecture' website wich
is all about sustainable design. You can also use the energy usage
test scaffold downloadable here to find out where energy
is being wasted!
|

PEAK ENERGY 4-8PM

When everyone is at home at the same time we use a lot of
energy. Think about everyone cooking dinner, watching TV and doing
homework all at once. It can be hard for our power stations to keep
up with the demand. Sometimes energy companies have to build even
more power stations to meet peak demand, which costs heaps and
increases our greenhouse emissions.
How can we reduce our energy use during peak energy
hours?
Energy company Energex can show us how we can simply save
energy, reduce emissions and save money by turning off appliances
at peak times. Find out more!
Stuff to Check Out
DON'T FORGET THE SEVEN BILLION...
Some countries around the world use HEAPS of energy per person,
while others survive on little or no electricity at all. When we go
camping or when there's a blackout, we manage to survive, but for
many people in the world, living
without power is a part of everyday life.
CHECK OUT POLLINATE!
A group of wonderful young Australians are doing some
amazing
things with sol ar power over in India,
can you imagine doing your homework with a kerosene lamp? Pollinate
are giving thousands of children access to power so they can have a
light at night time! Check
out what they are up to!
ar power over in India,
can you imagine doing your homework with a kerosene lamp? Pollinate
are giving thousands of children access to power so they can have a
light at night time! Check
out what they are up to!
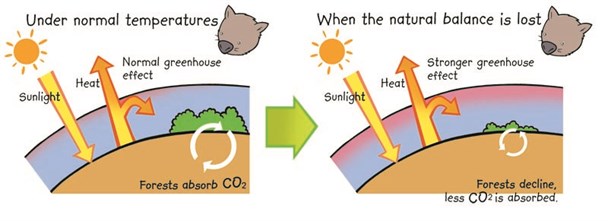
THE GREENHOUSE EFFECT
There are some gases in our atmosphere that capture heat
from the sun, we call them 'greenhouse gases'. The five main
greenhouse gases are steam, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide
and ozone. They act like a blanket around the planet and keep the
world at comfy temperatures.
Throughout history, temperatures on Earth have always changed.
They have risen and fallen because of natural causes like volcano
eruptions, changing ocean currents and variations in Earth's orbit
around the sun. But over the last century temperatures have
increased by 0.8 degrees Celsius - this is really fast compared to
historical changes.
Scientists who study this around the world have found that this
can only be explained by extra greenhouse gases produced by humans.
As population grows and people consume more, we need more energy,
so we burn more fossil fuels and release more greenhouse gases. The
greenhouse gas blanket is getting thicker and just like a great big
doona is trapping too much heat.